
Generic Postprocessing via Subset Selection for Hypervolume and Epsilon-Indicator*
Karl Bringmann1, Tobias Friedrich2, and Patrick Klitzke3
1Max Planck Institute for Informatics, Saarbrücken, Germany
2Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Jena, Germany
3Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken, Germany
Abstract. Most biobjective evolutionary algorithms maintain a population of fixed size 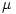 and return the final population at termination. During the optimization process many solutions are considered, but most are discarded. We present two generic postprocessing algorithms which utilize the archive of all non-dominated solutions evaluated during the search. We choose the best
and return the final population at termination. During the optimization process many solutions are considered, but most are discarded. We present two generic postprocessing algorithms which utilize the archive of all non-dominated solutions evaluated during the search. We choose the best 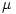 solutions from the archive such that the hypervolume or
solutions from the archive such that the hypervolume or 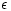 -indicator is maximized. This postprocessing costs no additional fitness function evaluations and has negligible runtime compared to most EMOAs.
-indicator is maximized. This postprocessing costs no additional fitness function evaluations and has negligible runtime compared to most EMOAs.
We experimentally examine our postprocessing for four standard algorithms (NSGA-II, SPEA2, SMS-EMOA, IBEA) on ten standard test functions (DTLZ 1–2,7, ZDT 1–3, WFG 3–6) and measure the average quality improvement. The median decrease of the distance to the optimal 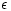 -indicator is 95%, the median decrease of the distance to the optimal hypervolume value is 86%. We observe similar performance on a real-world problem (wind turbine placement).
-indicator is 95%, the median decrease of the distance to the optimal hypervolume value is 86%. We observe similar performance on a real-world problem (wind turbine placement).
*The research leading to these results has received funding from the Australian Research Council (ARC) under grant agreement DP140103400 and from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no 618091 (SAGE). K.B. is a recipient of the Google Europe Fellowship in Randomized Algorithms, and this research is supported in part by this Google Fellowship.
LNCS 8672, p. 518 ff.
lncs@springer.com
© Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2014